Micro-arc Oxidation
Micro-arc oxidation, also known as micro-plasma oxidation, is a surface treatment process that combines an electrolyte with appropriate electrical parameters. It relies on the instantaneous high-temperature and high-pressure effects generated by arc discharge on the surfaces of aluminum, magnesium, titanium, and their alloys to grow a ceramic coating primarily composed of the base metal's oxides.
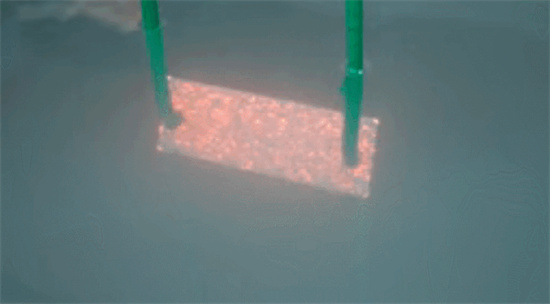
Metal Wire Drawing
Metal wire drawing is a surface treatment method that creates linear patterns on the workpiece surface through abrasion, achieving a decorative effect.

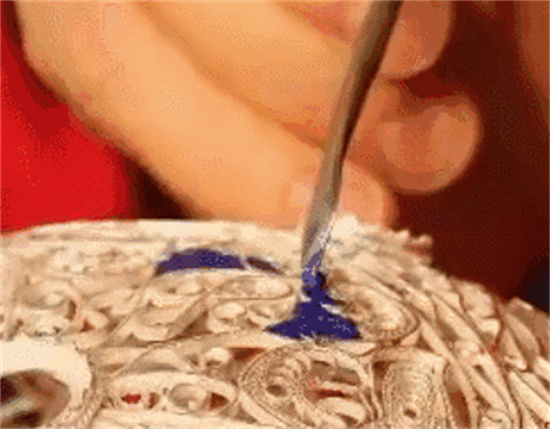
Cloisonné (Shao Lan)
Cloisonné involves filling the entire (base body) with colored glaze, which is then fired in a high-temperature furnace at around 800°C. The colored glaze transforms from a granular solid into a liquid, and upon cooling, solidifies onto the. Since the glaze is lower than the copper wire height, it needs to be refilled and fired again, typically four to five times, until the pattern is filled to the same level as the (cloisonné wire).

Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process that uses pellets to bombard the workpiece surface, implanting residual compressive stress and enhancing the fatigue strength of the workpiece.

Sandblasting
Sandblasting is a process that utilizes the impact of high-speed sand streams to clean and roughen the base surface. It employs compressed air as the power source to form a high-speed jet stream that propels abrasive materials (such as copper ore sand, quartz sand, diamond sand, iron sand, and Hainan sand) onto the workpiece surface, altering its appearance or shape.
Etching
Etching is a technique that removes material through chemical reactions or physical impacts. Commonly referred to as photochemical etching, it involves removing the protective film from the area to be etched after exposure and development, then exposing it to a chemical solution during etching to achieve dissolution and corrosion, resulting in concave, convex, or hollowed-out effects.

IMD
IMD, or In-Mold Decoration, also known as the paint-free technology, is an internationally popular surface decoration technology. It features a surface-hardened transparent film, an intermediate printed pattern layer, and a back injection layer, with the ink in the middle. This makes the product resistant to friction, prevents surface scratches, and maintains vivid colors that do not fade easily over time.
OMD
OMD, short for Out Mold Decoration, is an extension of IMD technology that integrates visual, tactile, and functional aspects. It is a 3D surface decoration technology that combines printing, texture structure, and metallization characteristics.

Laser Engraving
Laser engraving, also known as laser marking, is a surface treatment process that utilizes optical principles. It employs a laser beam to etch permanent marks on the surface of a material or within a transparent material.

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a special machining method that uses electrical erosion generated by pulsed discharges between two electrodes immersed in a working fluid to erode conductive materials. It is also known as spark erosion or electrical erosion machining. Tool electrodes are commonly made of materials with good conductivity, high melting points, and ease of processing, such as copper, graphite, copper-tungsten alloys, and molybdenum. During the machining process, the tool electrode also experiences wear, but it is less than the material removal from the workpiece, sometimes approaching negligible wear.
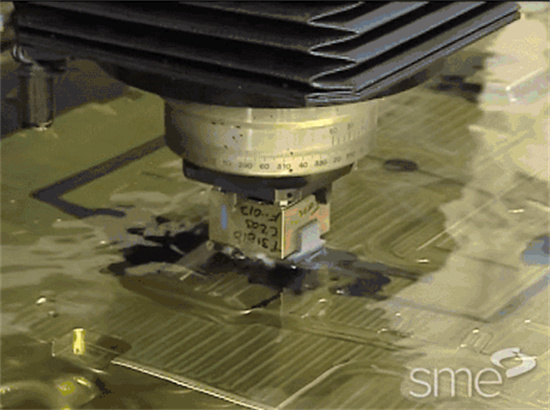
Laser Texturing
Laser texturing uses high-energy density lasers to react with the steel surface, creating patterns such as snake skin, etching, pear skin, or other forms of textures.

Pad Printing
Pad printing is one of the special printing methods. It uses a steel (or copper, thermoplastic plastic) intaglio plate and a curved pad head made of silicone rubber material. The pad head dips into the ink on the intaglio plate and then presses it onto the desired object's surface to print text or patterns.
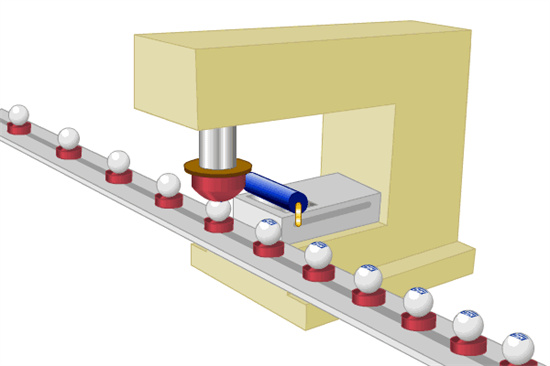
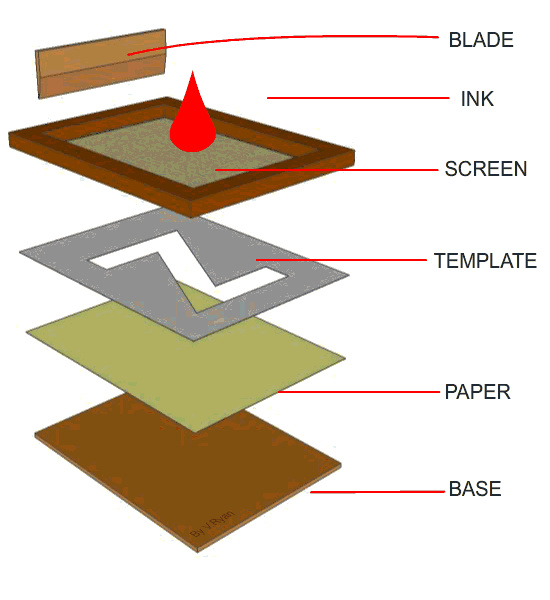
Screen Printing
Screen printing involves stretching a woven fabric, synthetic fiber fabric, or metal wire mesh onto a frame. A screen printing plate is created using manual paint scraping or photochemical plate-making methods. Modern screen printing technology uses photosensitive materials to create a screen printing plate through photographic plate-making (where the mesh holes in the graphic part of the screen printing plate are open, while the non-graphic part is blocked). During printing, ink is transferred through the mesh holes in the graphic part to the substrate using a squeegee, forming the same graphic as the original.
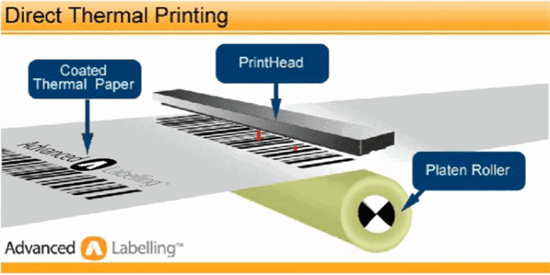
Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing involves coating a paper with a thermosensitive agent to create thermosensitive recording paper. When heat is applied, the thermosensitive recording paper undergoes physical or chemical changes in the substance (developer) to produce an image.
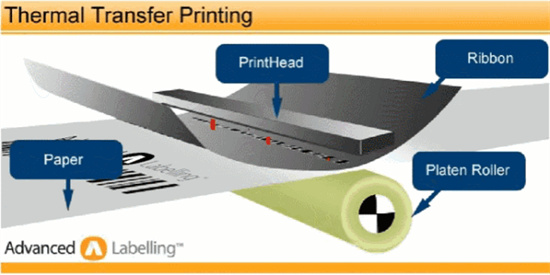
Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing involves printing digital patterns onto special transfer paper using a printer with special transfer ink. A dedicated thermal transfer machine then precisely transfers the pattern onto the (product) surface under high temperature and pressure, completing the product printing.
Offset Printing
In offset printing, the graphic and non-graphic parts of the printing plate are on the same plane. To distinguish between the inked and non-inked areas during printing, the principle of oil-water separation is utilized. First, a water supply device on the printing plate unit supplies water to the non-graphic part of the plate, protecting it from ink wetting. Then, an ink supply device supplies ink to the plate. Since the non-graphic part is protected by water, the ink only adheres to the graphic part. Finally, the ink on the plate is transferred to a blanket, and then to the substrate using the pressure between the blanket cylinder and the impression cylinder, completing the printing process. Thus, offset printing is an indirect printing method.
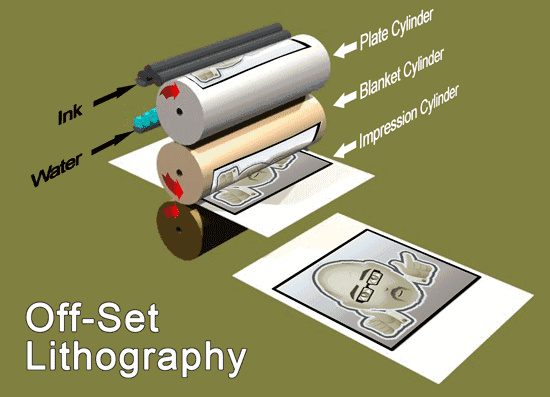
Curved Surface Printing
Curved surface printing involves placing ink into an intaglio plate engraved with text or patterns, then transferring the text or patterns onto a curved surface. The curved surface is then used to transfer the text or patterns onto the surface of a molded product. Finally, the ink is cured using heat treatment or ultraviolet light exposure.
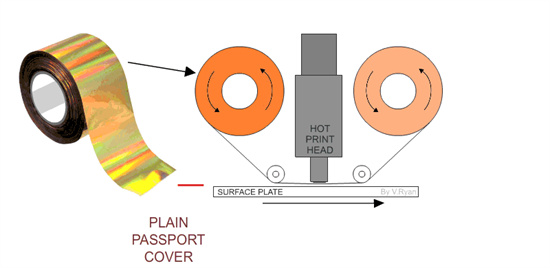
Hot Stamping
Hot stamping, commonly known as "foil stamping," involves stamping colored foil or other materials onto the front or back cover and spine of a hardcover book using heat and pressure to create text and patterns, or using a hot pressing method to emboss various convex or concave book titles or patterns.
Water Transfer Printing
Water transfer printing utilizes water pressure to hydrolyze transfer paper or plastic film with colorful patterns. The process includes making water transfer printing paper, soaking the paper, transferring the pattern, drying, and finishing the product.

Flat Screen Printing
The printing mold in flat screen printing is a fixed square frame with a stencil made of polyester or nylon mesh (screen plate) with hollowed-out patterns. The pattern areas on the screen plate allow color paste to pass through, while the non-pattern areas are sealed with a polymer film layer. During printing, the screen plate is pressed against the fabric, color paste is applied to the plate, and a squeegee is used to scrape back and forth, allowing the color paste to pass through the pattern and reach the fabric surface.

Calendering (also known as Pressing)
Calendering is the final process in heavy leather finishing. It utilizes the plasticity of fibers under heated conditions to flatten the fabric surface or press out parallel, fine, dense diagonal lines to enhance the fabric's luster. The material is fed in, heated and melted, then formed into sheets or films, cooled, and rolled up. The most commonly used calendering material is polyvinyl chloride.
AMTD provides high-precision Showerhead services for core components. Its products mainly include Shower head, Face plate, Blocker Plate, Top Plate, Shield, Liner, pumping ring, Edge Ring, and other semiconductor equipment core parts. These products are widely used in semiconductor, display panel, and other fields, with excellent performance and high market recognition.
Information Source: Hot Working Forum







